Systematic Review of Future Global Food Consumption Trends and Their Consequences (2025–2035)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70162/mijmsr/2024/v10/i1/v10i101Keywords:
Global food consumption trends; Technological advancements; Environmental impact; Socio-economic factors; Sustainable food systemsAbstract
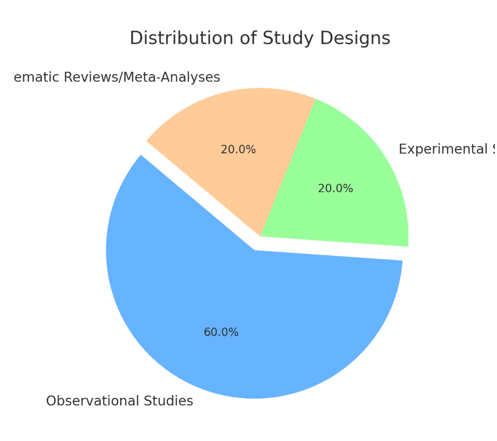
Background: The rapid evolution of food technologies, growing environmental concerns, and socio-economic disparities are reshaping global food consumption patterns. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing sustainable and equitable food systems. Objective: This systematic review aims to explore how technological advancements, environmental issues, and socio-economic factors influence global food consumption trends from 2025 to 2035. Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted across multiple databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, covering studies published between 2010 and 2023. Inclusion criteria focused on studies addressing technological, environmental, or socio-economic impacts on food consumption. The quality of included studies was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool and the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Data were synthesized thematically. Results: The review found that precision agriculture, alternative proteins, and food processing technologies are driving significant changes in dietary patterns. Environmental concerns, such as greenhouse gas emissions and water use, are leading to a shift towards plant-based diets. Socio-economic factors, including income, education, and cultural norms, continue to shape food choices. Conclusion: These findings underscore the need for policies and practices that support sustainable food technologies and address socio-economic disparities. Further research is needed to explore the long-term sustainability of these trends and their socio-economic implications.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
License Terms
Macaw International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research is committed to promoting the dissemination of knowledge through open access while ensuring that authors retain key rights to their work. The license terms under which your work is published play a crucial role in achieving this balance.
1. Open Access License
All articles published in Macaw International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research under the open access model are made available under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). This license allows for the broadest possible dissemination of your work while ensuring that you, as the author, receive proper credit for your contribution.
Key Features of the CC BY License:
- Attribution: Others may distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon your work, even commercially, as long as they credit you for the original creation.
- Freedom to Share and Adapt: This license encourages the wide sharing and adaptation of your research, promoting greater impact and visibility.
- Commercial Use: The CC BY license permits others to use your work for commercial purposes, provided that appropriate credit is given.
2. Copyright and Author Rights
When you publish with Macaw International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research, you retain significant rights to your work, even after publication.
2.1 Copyright Transfer
- Upon acceptance of your manuscript, you will be asked to transfer the copyright of your work to the journal. This transfer is necessary to enable the journal to publish, distribute, and archive your work.
- Despite the transfer of copyright, you retain the right to:
- Reuse Your Work: Use your published work in future research, presentations, or compilations of your work, such as in your dissertation or a future book.
- Post on Repositories: Deposit the final published version of your article in institutional or subject-based repositories, including your personal or institutional website.
- Distribute to Colleagues: Share your published article with colleagues or use it for educational purposes.
3. Reuse of Published Content
Under the CC BY license, third parties are free to reuse content published in Macaw International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research as long as they provide appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source of publication.
3.1 Conditions for Reuse:
- Attribution: All reused content must include a full citation to the original article published in our journal.
- No Endorsement: The reuse of content must not imply endorsement by the authors or the journal without explicit permission.
- Modifications: If the content is modified or adapted, this must be clearly indicated, and the changes must be appropriately credited.
4. Author Warranties
By submitting a manuscript to Macaw International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research, you warrant that:
- Originality: The work is your original creation and does not infringe upon the rights of others.
- Exclusive Submission: The manuscript is not under consideration for publication elsewhere and has not been previously published.
- Ethical Compliance: All research involving human participants, animals, or other subjects complies with ethical standards and has received the necessary approvals.
5. Exceptions and Special Licenses
In some cases, specific articles or content types may be published under different license terms, such as those required by funding agencies or other third parties. Any such exceptions will be clearly noted in the published work.





